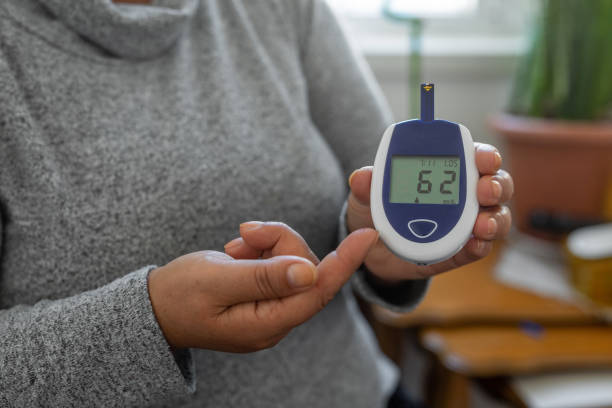
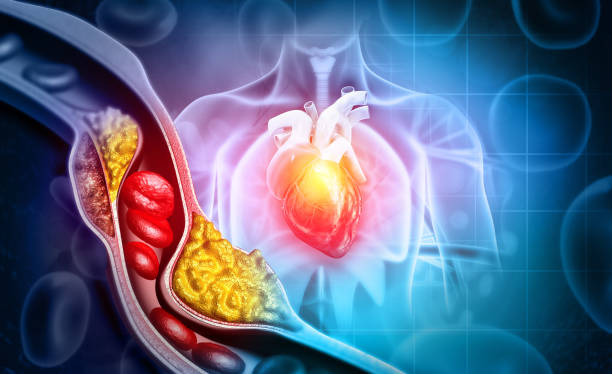
High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, is indeed a significant concern associated with diabetes. It can lead to various complications, including those you mentioned like heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. The inability of the body to produce enough insulin or effectively utilize it is a hallmark of diabetes. The prevalence rates you mentioned from the CDC underscore the magnitude of this health issue in the United States. Managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, medication, and lifestyle modifications is crucial for individuals with diabetes to prevent complications and maintain overall health.
It’s crucial for people living with diabetes to actively manage their blood sugar levels to prevent complications. Regular monitoring, exercise, and adhering to a personalized diet plan are indeed vital components of managing blood sugar effectively.
Hyperglycemia, indicated by blood sugar levels over 180 mg/dL, requires prompt attention to bring levels back within the target range. Failing to do so can lead to both short-term and long-term complications, as you mentioned.
1. Regular Exercise for blood sugar
Regular exercise is a cornerstone of diabetes management. It helps to improve insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to more efficiently utilize glucose, thus lowering blood sugar levels. The variety of exercises you mentioned, such as weightlifting, brisk walking, running, cycling, dancing, hiking, and swimming, are all excellent options. The key is to find activities that you enjoy and can incorporate into your routine consistently. This not only helps with blood sugar management but also promotes overall health and well-being. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have diabetes or other underlying health conditions for blood sugar
2. Reduce carbohydrate intake
Reducing carbohydrate intake can indeed be an effective strategy for managing blood sugar levels, as carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood glucose levels compared to other macronutrients. Adopting a low-carb dietary pattern may help individuals with diabetes stabilize and manage their more effectively.
However, it’s essential to recognize that dietary changes, especially ones as significant as reducing carbohydrate intake, may not be suitable for everyone . Some individuals may find it challenging to maintain a low-carb diet in the long term, and certain medical conditions or individual health needs may require adjustments to this approach.
Therefore, consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes is crucial. They can provide personalized guidance and support tailored to individual health goals and medical needs, ensuring that any dietary changes are safe, effective, and sustainable in the long run.
3. Weight Mangement
Maintaining a moderate weight is indeed important for managing diabetes effectively. Research consistently shows a correlation between obesity and type 2 diabetes, as well as insulin resistance, which is a key factor in diabetes development and management blood sugar
By achieving and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can improve their body’s sensitivity to insulin, making it easier for glucose to enter cells and thus helping to regulate blood sugar levels more effectively.
It’s worth noting that the ideal weight range varies from person to person based on factors such as age, height, muscle mass, and overall health status. Consulting with a doctor or a healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance on achieving and maintaining a healthy weight tailored to individual needs and circumstances. They can also offer support and resources to help individuals reach their weight management goals safely and effectively.
4. Plenty Water
Drinking plenty of water is indeed essential for overall health, including for individuals managing diabetes. Adequate hydration supports kidney function, helping to flush out excess sugar from the bloodstream and maintain proper hydration levels, which is crucial for overall well-being.
Research has suggested a link between higher water intake and a reduced risk of developing high blood sugar levels, emphasizing the importance of staying well-hydrated as part of diabetes management. It’s important to note that water is the best choice for hydration, as sugary drinks can elevate blood sugar levels further and may contribute to other health issues if consumed excessively. Encouraging individuals with diabetes to prioritize water consumption and limit intake of sugary beverages can be beneficial for managing blood sugar levels and promoting overall health.
5. Portion Control
Eating moderate portions is indeed crucial for managing weight and promoting healthy blood , especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Controlling portion sizes helps to regulate calorie intake, which is essential for achieving and maintaining a moderate weight. By managing weight effectively, individuals can improve their body’s sensitivity to insulin, reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, and better control blood sugar levels. Adopting portion control strategies such as using smaller plates, measuring servings, and paying attention to hunger and fullness cues can help individuals make healthier food choices and avoid overeating. Incorporating a balanced diet consisting of nutrient-dense foods in appropriate portions is key to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight and supporting overall health, including managing blood sugar levels effectively.
6. Managing stress
Regular physical activity is particularly beneficial, as it not only helps to reduce stress but also improves insulin sensitivity and promotes weight management, all of which contribute to better blood sugar regulation. Incorporating stress management techniques into daily routines can be valuable for individuals with diabetes, helping them to better manage their condition and improve overall quality of life.
7. Enough Sleep
Getting enough sleep is crucial for overall health and can significantly impact blood sugar levels, especially for individuals managing diabetes or concerned about their blood sugar.
Poor sleep habits, such as inadequate sleep duration or disrupted sleep patterns, can disrupt hormonal balance, including increasing levels of cortisol, the stress hormone. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to increased appetite, promote weight gain, and negatively affect blood sugar regulation.
Research has shown that sleep deprivation can impair insulin sensitivity, making it more challenging for the body to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Additionally, inadequate sleep can disrupt the body’s circadian rhythm, which plays a role in regulating metabolism and blood sugar control.
Therefore, prioritizing good sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques before bedtime, can help promote better sleep quality and support optimal blood sugar management.
8. Consume foods abundant in chromium and magnesium.
Consuming foods rich in chromium and magnesium can indeed be beneficial for managing blood levels, as both minerals play important roles in regulating glucose metabolism.
Chromium helps enhance the action of insulin, promoting the uptake of glucose into cells and thereby assisting in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Foods rich in chromium include meats (especially liver), fruits, vegetables (such as broccoli and potatoes), nuts, and whole grains.
Magnesium is also involved in glucose metabolism and insulin action, and deficiency in magnesium has been associated with insulin resistance. Consuming foods rich in magnesium, such as dark, leafy greens (like spinach and kale), seeds (such as squash and pumpkin seeds), fish (like tuna), whole grains, dark chocolate, bananas, and beans, can help support healthy blood sugar levels.
Incorporating a variety of these foods into your diet can contribute to overall health and help support optimal blood sugar regulation. However, it’s essential to maintain a balanced diet and consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary recommendations, especially if you have specific health concerns or conditions like diabetes.
9. Eating smaller, balanced meals
Eating smaller, balanced meals and snacks throughout the day can indeed help maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent spikes that may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. Choosing healthy snacks like fruits, nuts, yogurt, or vegetables with hummus can provide a steady source of energy without causing dramatic fluctuations in blood sugar levels. Plus, spreading out your meals and snacks can also help regulate appetite and prevent overeating during main meals. It’s a win-win for both your blood sugar and overall health